Periodontal Disease & Cell Migration
Cell migration assays allow scientists and researchers to measure cell migration patterns. Platypus Technologies Oris Pro cell migration assays support many different cell types with extracellular matrix coated wells. In addition, Oris stoppers can be used to create cell free detection zones.
A research study investigating the effects of dual zinc plus arginine on tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) utilized Platypus Technologies Oris cell migration assay. TNF-α is a cytokine present in infected periodontal tissue. This cytokine is able to direct tissue and bone destruction contributing to periodontal diseases. Periodontal disease is an inflammatory infection that can cause serious health implications if left untreated. This gum disease has been shown to damage gum tissue and affect the bone supporting teeth. A pathogen known as gram-negative anaerobic bacteria facilitates periodontal disease which is then followed by an inflammatory response to immune cells. In this response, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) begin degrading extracellular matrix proteins.
A B11 immortalized human gingival keratinocyte cell line was used to indicate a potential protective effect of Dual Zinc plus Arginine solution. Cells were cultured with a keratinocyte medium with growth factors and penicillin. Transepithelial electrical resistance (TER) was used to quantify keratinocyte barrier integrity. Keratinocytes play a significant role in pathogen prevention by helping build the epidermis which provides a natural barrier.
Keratinocytes were immunostained with two tight junction proteins (occludin and zonula occudens-1) and incubated to allow cell adhesion to occur. Immunofluorescence staining was used to visualize the effect of Dual Zinc on the two tight junction proteins. Cells were then either treated with TNF-α or not and cell proliferation was measured.
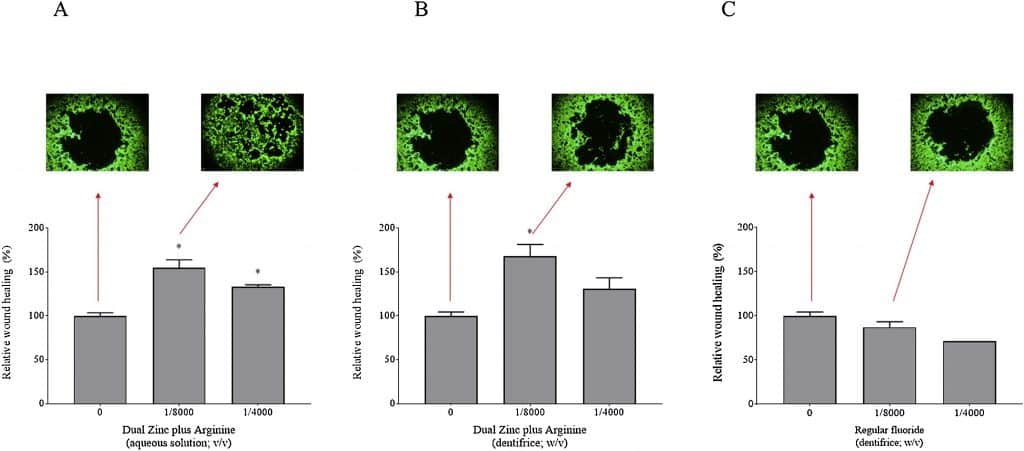
An Oris Pro cell migration Assay Kit was used to determine keratinocyte migration when exposed to Dual Zinc plus Arginine. Cells were seeded into the 96-well microplate in which type I collagen coated wells with stoppers provided a designated migration area. Cell migration was determined with a microplate reader.
The results generated from the migration assay indicated that exposing gingival keratinocytes with TNF-α decreased TER values. Increased paracellular transport of fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated dextran of 4.4 kDa (FD-4) was also observed. Dual zinc plus arginine solutions prevented the decrease of TER values caused by TNF-α. The figure below illustrates how dual zinc plus arginine prevented the irregular cell distribution of the two tight junction proteins. TNF-α causes dysfunction to the gingival keratinocyte barrier through the production of tight function proteins. Tight junction proteins are able to efficiently produce due to their ability to adhere to other tight junction protein molecules. The immunofluorescent stains show that TNF-α alone caused an irregular cell distribution while Dual Zinc plus Arginine prevented this distribution from occurring.
Results also indicated that TNF-α reduces cell proliferation. However, Dual Zinc plus Arginine was able to combat this by allowing for increased cell proliferation and cell migration.
This research indicated that Dual Zinc plus Arginine is able to successfully prevent the periodontal based damages caused by TNF-α.
Reference: